Exercises: Graph Data Structures
Mar 052018Before attempting these exercises, you should read the posts about graphs, graph problems, and graph data structures.
Exercises
- The following Python code represents a graph using the edge list data structure.
Draw a node/link diagram for the graph.
nodes = ['node1', 'node2', 'node3', 'node4'] edges = [ ('node1', 'node3'), ('node1', 'node4'), ('node2', 'node2'), ('node3', 'node4'), ('node4', 'node2') ] - The following Python code represents a graph using the adjacency list data structure.
Draw a node/link diagram for the graph.
class Node: def __init__(self, value): self.value = value self.neighbours = [] def add_neighbour(self, node): self.neighbours.append(node) def __repr__(self): fmt = 'Node({!r})' return fmt.format(self.value) node1 = Node(1) node2 = Node(2) node3 = Node(3) node4 = Node(4) node1.add_neighbour(node2) node1.add_neighbour(node3) node3.add_neighbour(node4) node4.add_neighbour(node4) - The following Python code represents a graph using the adjacency matrix data structure.
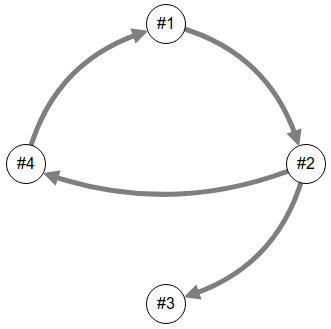
Draw a node/link diagram for the graph, labelling the nodes “#1”, “#2”, “#3” and “#4”.
adjacency_matrix = [ [0, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0] ] - Write Python code to represent the following graph using each of the three graph data structures.


There are no published comments.